JWT Attacks & Token Entropy Analysis with Burp Sequencer
Summary
Today I focused on JSON Web Token (JWT) security weaknesses and how improper implementations can lead to authentication bypass and privilege escalation.
I explored common JWT attack vectors and used Burp Suite’s Sequencer to evaluate token randomness and entropy.
This provided hands-on experience in assessing the strength of token-based authentication mechanisms.
Background: Why JWT Security Matters
JWTs are not encrypted by default — they are only Base64URL-encoded.
This means anyone can read the header and payload.
The security of JWT-based authentication depends entirely on strict signature verification and proper cryptographic configuration.
A single misconfiguration can result in:
- Authentication bypass
- Privilege escalation
- Full API compromise
JWT Structure & Common Weaknesses
A JWT consists of three parts:
1
2
3
HEADER.PAYLOAD.SIGNATURE
I studied several dangerous implementation mistakes:
- Accepting tokens without verifying the signature
- Allowing algorithm confusion (e.g., RS256 → HS256)
- Using weak or predictable secrets with HS256
- Generating low-entropy or predictable tokens
These issues can allow attackers to forge valid tokens.
Attacks Practiced
1. alg: none Attack
By modifying the JWT header:
1
{ "alg": "none" }
and removing the signature entirely, some weak backends incorrectly accepted the token as valid.
Impact: Authentication bypass and user impersonation.
2. Algorithm Switching (RS256 → HS256)
When the backend does not strictly enforce the signing algorithm:
- The RSA public key can be reused as an HMAC secret
- A forged token becomes valid
Impact: Full token forgery and privilege escalation.
3. Brute-Forcing Weak Secrets (HS256)
Using jwt_tool with a wordlist:
1
jwt_tool TOKEN -C -d wordlist.txt
I simulated brute-force attacks against weak secrets. Short or predictable secrets were cracked quickly.
Impact: Permanent compromise of authentication.
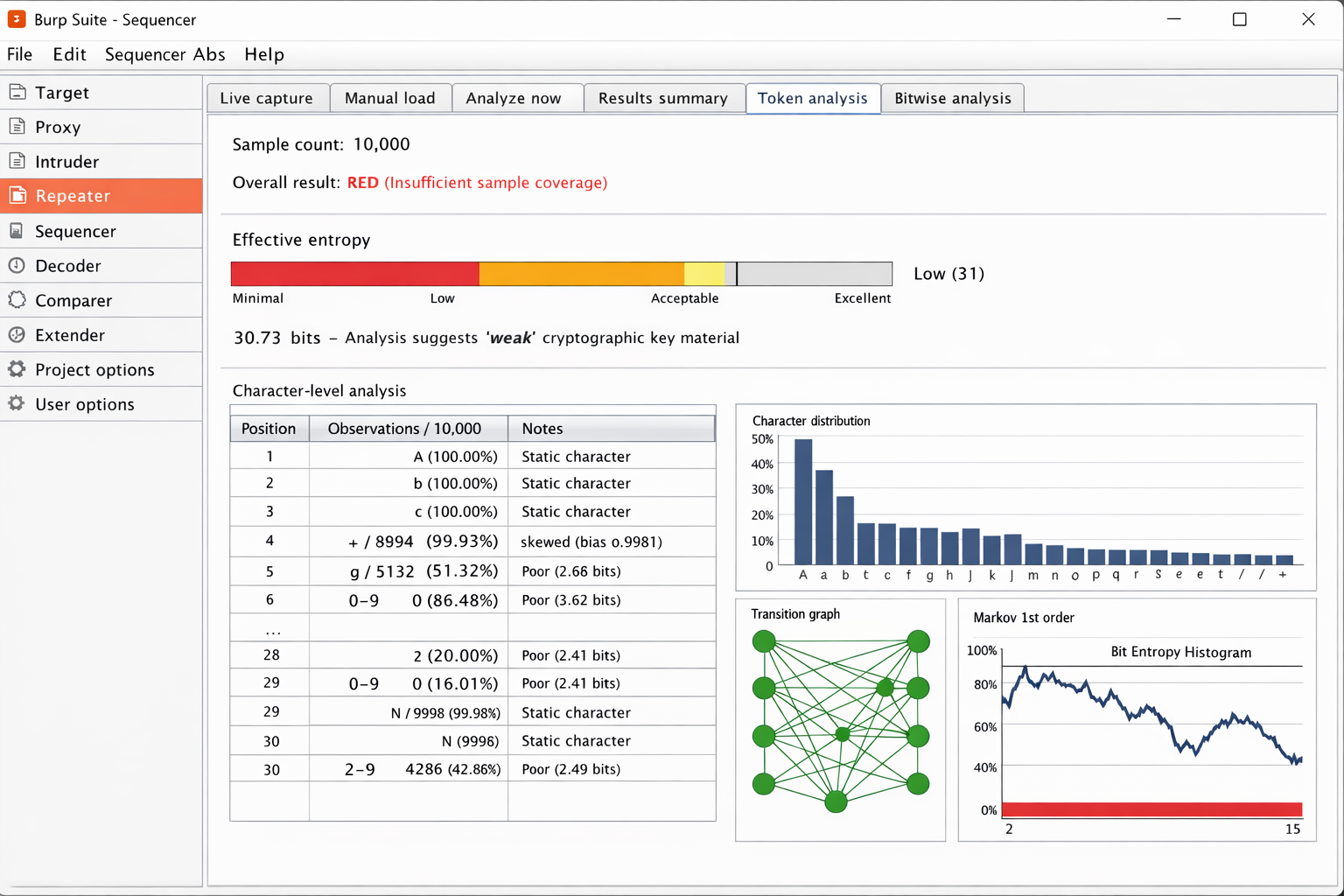
Token Entropy Analysis with Burp Sequencer
I sent JWT responses to Burp Suite’s Sequencer and collected a large number of samples.
Sequencer revealed:
- Low effective entropy
- Static characters at the beginning of tokens
- Predictable structure
This indicates that tokens could potentially be guessed or brute-forced.
Tools Used
- Burp Suite (Sequencer)
- jwt_tool
- Postman
Security Impact
Weak JWT implementations can lead to:
- Account takeover
- Privilege escalation
- Complete API compromise
JWTs should be treated as critical security components, not simple session tokens.
Prevention & Best Practices
- Always enforce signature verification
- Disable the
alg: noneoption - Lock the signing algorithm on the backend
- Use long, random secrets for HS256
- Prefer asymmetric algorithms (RS256) with proper key management
- Regularly test token randomness using tools like Burp Sequencer
Key Takeaway
JWT security is not about using JWTs — it’s about how strictly they are validated.
Weak validation turns authentication into an illusion.